Bronsted Acid Vs Lewis Acid
Acids and bases play vital roles in many organic chemical reactions. This page examines two complementary definitions of acids and bases, and explores some of the more common ways in which acids and bases are involved in promoting organic reactions. The factors that influence the relative strengths of acids and bases are as well reviewed.
Strongly Related Topics
- Concrete Backdrop of Organic Compounds
- Free energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions
- Resonance and Resonance Forms: Conjugation and Conjugated Systems
- Isomers/Isomerism
Somewhat Related Topics
- Carbocations
- Additions to Alkenes: Regiochemistry
- E2 Reactions
- Tautomers/Tautomerism
Glossary Terms
| acidity constant | Bronsted-Lowry acids | Bronsted-Lowry bases |
| conjugate acid | conjugate base | electrophile |
| Human being | Lewis acrid | Lewis base |
| LUMO | nucleophile | resonance event |
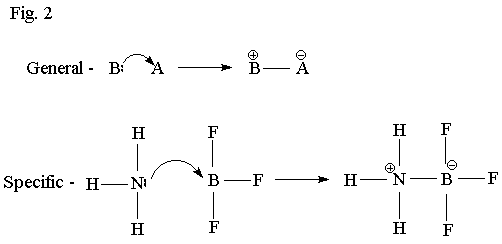
Acids and Bases: Lewis vs. Bronsted
There are two complementary definitions of acids and bases that are important:
- the Bronsted (or Bronsted-Lowry) definition: an acid is a proton (H+ ion) donor, and a base is a proton acceptor;
- the Lewis definition: an acrid is an electron acceptor, and a base is an electron donor.
Fig. 1


Self-Test Question #1 Below are shown ii very similar acid/base reactions:

In each case, decide which of the reactants is a base, and which is an acid. Likewise make up one's mind which procedure is a Lewis acid/base reaction, but is not a Bronsted-Lowry acrid/base reaction.
Links to Related reading in textbook (McMurry, Organic Chemical science, 4th ed.)
- Chapter two, Section 2.half dozen: pages 50-59
- Chapter 20: pages 774-801
- Chapter 24, Department 24.four: pages 941-945
Links to Related Computer-based Learning Materials
- Links to Related Chem TV Files
- Vol.1,Topic four: Functional Groups
- Vol.ii,Topic 4: Carboxylic Acids/Derivatives
- Vol.2,Topic 5: Amines
- Links to Related 30 Files
- Links to Related yyy Files
- Links to Related zzz Files
- Related Beaker Menu Fuctions
- Struct, "Functional Groups"
- React, "Hydrogen pKa"
- React, "Perform a Reaction"
Links To Related Internet Resources
- Organic Chemistry ConcepTests
Dr. Thomas H. Eberlein
the1@psu.edu
Copyright � 1996 Thomas H. Eberlein
Version one.2.v, 3/17/97
Bronsted Acid Vs Lewis Acid,
Source: https://canov.jergym.cz/ph/vedci/lb.htm
Posted by: callahanwassaimmat44.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Bronsted Acid Vs Lewis Acid"
Post a Comment